In a February 9, 1970 Barron’s article titled “600 on the Dow?” William X. Scheinman provides an interesting chart of the Dow Industrials (DJI) that outlines what he believes to be the target level that the DJI would fall to before rebounding. This analysis included macro economic analysis that supported the reasons why the Dow was expected to go to 600.
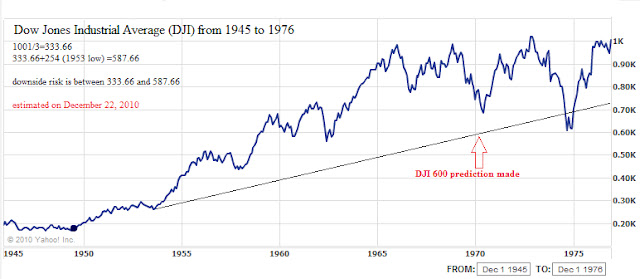
What is most compelling in Scheinman’s analysis is the accuracy of the target level that the DJI was expected to reach. An element that leaves some unanswered questions is that Scheinman had predicted that the DJI would reach 600 within the same year that the article was written. Of course, The DJI didn’t reach 600 until 1974. This has to do with Scheinman’s cycle analysis which is separate and distinct from the topic which we will examine. Being aware of this inconsistency and leaving it aside for the time being, we’ve attempted to understand the rational and methodology of how Scheinman was able to arrive at 600 on the DJI when it was trading at 755.68.
Scheinman indicates that he obtained his method for accurately predicting the level of the DJI from Edson Gould. According to Scheinman, Gould used what is known as the 1/3 speed resistance line measurement to gauge price change and elapsed time which was purported to be two key determinants of crowd psychology in the market. Scheinman goes on to say:
“Resistance lines decline or ascend at one-third or two-thirds the rates of actual declines and advances between significant bottoms and tops. Resistance to advance or decline is frequently encountered at such trendlines; however, if the resistance line is decisively penetrated, the price-action often tends to accelerate in the direction of the penetration.”
In an example provided by Scheinman below, he plots the bull market of the DJI from 1949 to 1970. In that chart, we can see that the dashed line, the one-third speed resistance line, intersects with the 600 level on the DJI.
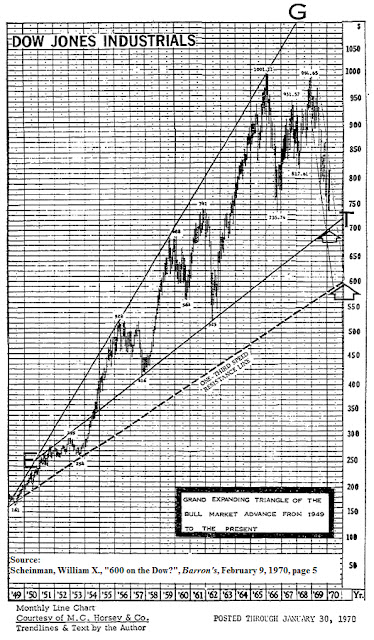
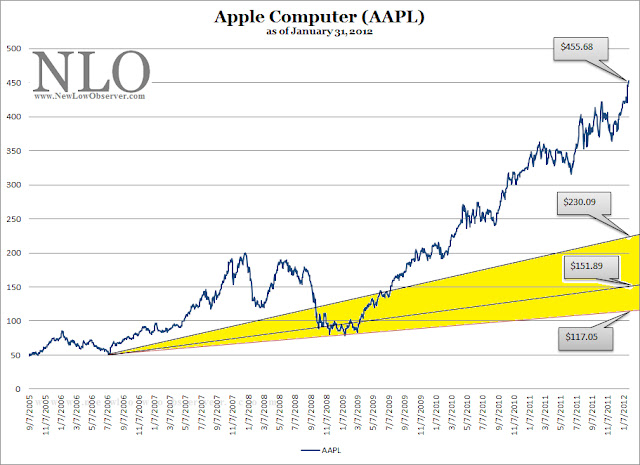
As far as we can tell, the 1/3 speed resistance line is calculated by dividing the peak of the market move by 3. To be as conservative as possible, we’ve added the 1/3 speed resistance figure to the low of the first major decline in the bull run. In this case, the first major low in the bull market from 1949 to 1966 was at the 1953 low of DJI 254. The peak is indicated to be 1001 (1001/3=333.66). Then we add 333.66 to 254 arriving at a figure of 587.66. In order to account for the extremes, we assume that 1/3 the peak is the point at which the market finally settles. In this case, 1/3 of the peak value is 333.66. We feel that the conservative and extreme values help to establish a range which a market or stock that has had a near parabolic rise will finally settle at or near.
According to our calculations for the market run from 1949 to 1966, 587.66 and 333.66 were the conservative and extreme downside targets for the market, respectively. However, in the article, Scheinman says that the potential worst-case scenario level would be 597.61. For the most part, Scheinman’s estimate was fairly accurate in terms of where the reversal in the market occurred. The bottom in the stock market took place on December 9, 1974 at the 579.94 level.
In the chart of the Dow from 1945 to 1976 below, it should be noted that a large amount of “overshooting” of the 1/3 speed resistance line occurred when the low did take place in 1974 instead of 1970 as predicted by Scheinman. In the case of the Dow, the index overshot the 1/3 speed resistance line in 1974 by 15%. However, the price was well within the established, albeit wide, range of 587.66 to 333.66.
We decided to see how consistent the 1/3 speed resistance line would be if applied to three different situations. First, we’ll review the bull market in the Dow Industrials (DJI) from 1982 to 2007. Next, we’ll run this model using the Philadelphia Gold and Silver Index (XAU) from the bear market bottom of 2001 to the present. Finally, we’re going to see how this model works against Netflix (NFLX), a member of the Nasdaq 100, in a real-time example.
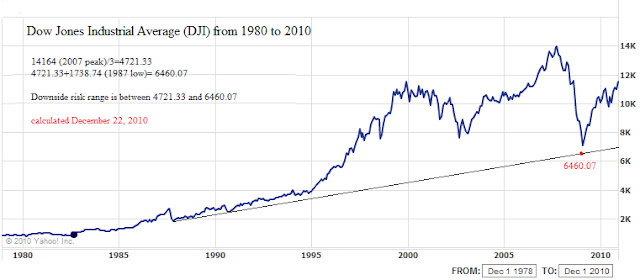
In the case of the bull market run from 1982 to 2007, we divided the peak of the market at 14,164 by 3 and arrived at 4721.33. We then added 4721.33 to the first major low in the market after the beginning of the bull market which was in 1987 at 1738.74. The sum of the two figures is 6460.07 for the conservative and 4721.33 for the extreme scenarios.
When we review the actual bottom in the DJI in 2009 of 6547.05 we can see that the difference between the most conservative estimate and the 2009 low was off by 86.98 points. There is no instance of the DJI overshooting the 1/3 speed resistance line. Although coming within 1.5% of an estimated target seems exceptional, the real challenge becomes, would an investor commit money to an investment before the price level actually hits a projected target? Once invested, could an investor stomach a further decline of 27% or more? [(6460.07-4721.33)/6460.07=26.92%]
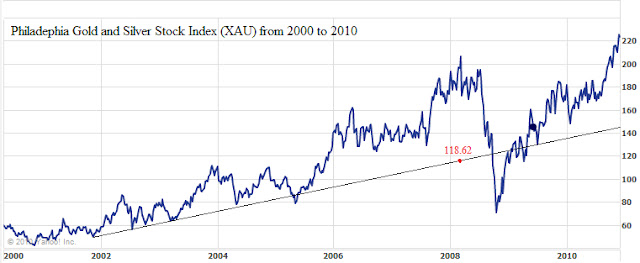
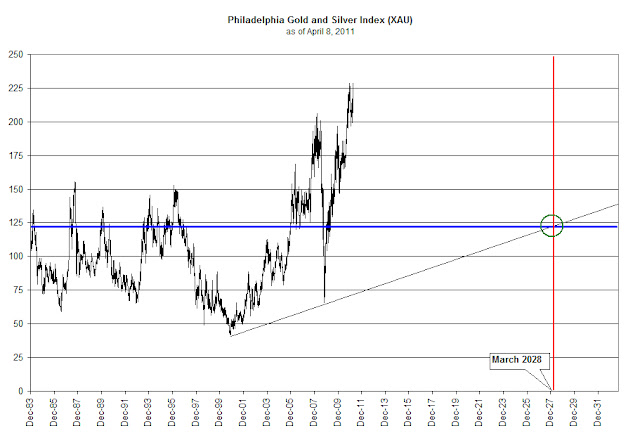
In the case of the bull market run in the XAU Index, we divided the peak of the index at 206.37 in 2008 by 3 and arrived at 68.79. We then added 68.79 to the first major low in the index after the beginning of the bull run, which was at 49.83 on November 19, 2001. The sum of the two figures is 118.62. When we contrast the difference between the two numbers, 118.62 and the actual low of 65.72, we see that conservative estimate was accomplished, however a further decline of 45% to below the extreme level was established instead. Reasonably near the extreme end of the range, but who is willing to hold on after a 45% drop?
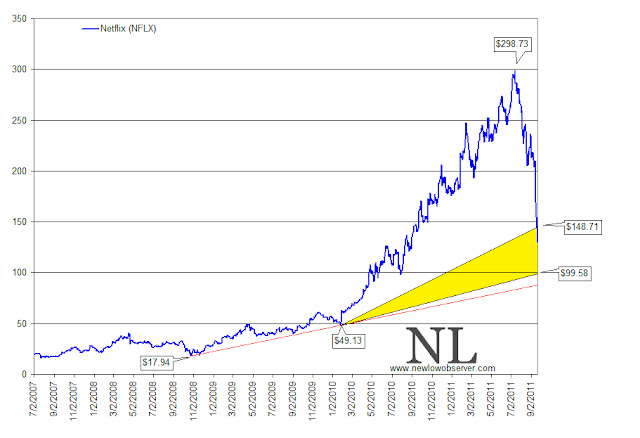
Finally, in reviewing the chart pattern of Netflix (NFLX), we have the peak of NFLX at $298.73. The conservative estimate for the stock is that it would fall to $148 which has already taken place. The extreme downside target would be $99.58. Because of the nature of the rise, we believe that Netflix (NFLX) is slated to fall at least to the $99.58 level.
If for any reason investors become interested in buying Netflix (NFLX), the ideal time to do it appears to be at a price at or below $99.58. However, the difficulty may be that the sentiment that pushed the stock price to $298.73 would likely be just the opposite to push the price down. Only time will tell whether Netflix is going to conform to technical patterns created by Edson Gould.
Please consider donating to the New Low Observer. Thank you.